I. 서 론
알코올은 사회 전반에 상당한 건강, 사회 및 경제적 부담을 초래하는 물질로, 전 세계적으로 매년 300만 명이 알코올로 인해 사망한다1. 우리나라의 1인당 알코올 소비량은 9.1 L로 OECD 국가 평균인 9.0 L의 국가의 평균적인 수준이나, 최근 들어 주류 소비량이 증가 추세이다. 최근 국내 음주실태를 살펴보면 여성 음주율이 증가하고 있으며, 20-30대의 고위험 음주율이 높고, 1회 음주량이 적정 음주량에 대비하여 높은 특징을 보여 그 위험성이 증가되고 있다2. 지속적인 알코올의 과다 섭취는 급성 중독뿐만 아니라 위장관, 췌장, 간, 대사장애, 심혈관 등에 영향을 미쳐 다른 질병이나 부상의 원인이 된다3. 알코올성 간질환(Alcoholic Liver Disease, 이하 ALD)은 알코올로 인한 사망의 가장 주요한 원인으로 알코올성 지방간, 간염, 간경변증의 다양한 범주를 포함하는 질환군을 의미한다3,4. ALD의 병리생리학의 이해에서 많은 발전이 있었음에도 불구하고 그 치료는 50년 전과 비교하여 큰 발전이 없는 실정으로, 가벼운 알코올성 지방간과 염증은 금주에 가역적으로 반응하나 심한 알코올성 지방간염, 간경화, 간세포 암으로 진행된다면 예후는 좋지 않다3.
한의학에서는 ALD를 酒傷으로 보고 發散汗出하고 利小便하여 濕毒을 上下로 分消하는 치법을 사용하여 치료해 왔으며5 실험적, 임상적 연구를 통해 그 유효성 및 안전성에 대한 연구가 이루어지고 있다. 그러나 연구 결과 보고 자체가 부족하여 최근 10년간 국내 한의학 학술지에 게재된 임상 논문은 14편6,7,12-14,16,18-20,22-26에 불과하다. 특히 대부분이 증례보고에 그치며 무작위임상시험 논문은 단 1편28 뿐이다. 이에 저자는 국내의 ALD에 대한 연구들을 살펴 한의학적 치료에 근거를 마련하고 향후 연구의 방향성을 제시하기 위해 국내 논문 데이터베이스를 통해 검색한 자료를 정리하였다.
II. 연구대상 및 방법
1. 연구 대상
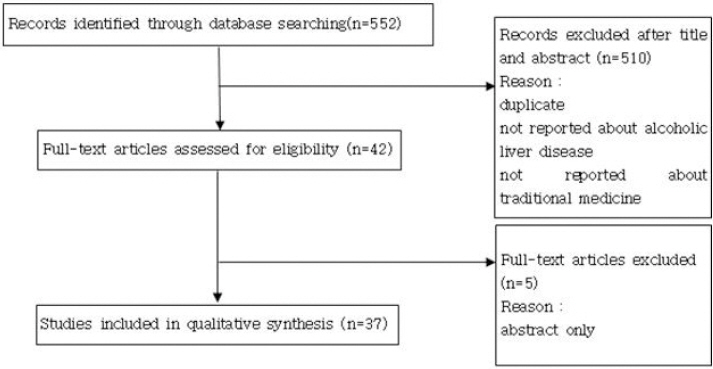
논문 검색은 국내 논문 데이터베이스 중 과학기술정보통합서비스(http://www.ndsl.kr), 한국의학논문데이터베이스http://kmbase.medric.or.kr), 한국전통지식포탈(http://www.koreantk.com), 한국학술정보(http://kiss.kstudy.com), 과학기술학회마을(http:// society.kisti.re.kr), KoreaMed(http://www.koreamed.org)를 이용하였다. 검색 시 논문 발행 기간에 제한을 두지 않고 2019년 1월 31일까지 데이터베이스에 등록된 모든 문헌을 2019년 2월 1일부터 2019년 2월 3일까지 검색하였다. 검색 엔진 키워드는 ‘알코올성 간질환’, ‘알코올성 지방간’, ‘알코올성 간염’, ‘알코올성 간경변’, ‘alcoholic liver disease’, ‘alcoholic fatty liver’, ‘alcoholic hepatitis’, ‘alcoholic cirrhosis’, ‘herbal medicine’, ‘acupuncture’, ‘traditional medicine’을 사용하였다.
III. 결 과
1. 연도별 및 연구 유형별 분류
선정된 논문 37편을 출판 연도별로 살펴보면 2018년 6편(16.2%), 2017년 1편(2.7%), 2016년 3편(8.1%), 2015년 1편(2.7%), 2014년 1편(2.7%), 2012년 1편(2.7%), 2011년 1편(2.7%), 2010년 2편(5.4%), 2009년 5편(13.5%), 2008년 3편(8.1%), 2007년 1편(2.7%), 2004년 1편(2.7%), 2003년 1편(2.7%), 2001년 3편(8.1%), 2000년 3편(8.1%), 1999년 2편(5.4%), 1996년 1편(2.7%), 1993년 1편(2.7%)으로 논문이 발표 되었다. 그 중 실험논문 8편(21.6%), 임상연구 논문 26편(70.3%), 고찰논문 3편(8.1%)으로 임상 연구논문이 반 이상을 차지하였다. 임상연구 논문은 case report 17편(65.4%), case series 7편(26.9%), assessment scale(평가척도연구) 1편(3.8%), 무작위대조시험 1편(3.8%)으로 증례보고가 대부분이었다.
총 16종의 학회지에서 출판되었으며 이 중 13편(35.1%)이 대한한방내과학회로 가장 많았으며 동의생리병리학회에서 4편(10.8%), 대한한의학 방제학회지와 대한한의학회지에서 3편(8.1%)의 논문이 출판되었다(Table 1).
Table 1
The List of the Selected Studies
| Author | Year | Title | Journal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jeong YE6 | 2018 | A Case of Korean Medicine for Alcoholic Liver Disease Patients with Fatigue and Dizziness | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Bae JH7 | 2018 | A Case Study of Two Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis Patients | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Kim BK8 | 2018 | Effect of SAL5 on chronic ethanol-induced fatty liver model | Kor J Herbol |
|
|
|||
| Kim TH9 | 2018 | Hepatoprotective Effect of Bacillus subtilis-fermented Silkworm (BombyxmoriL.) Extract on an Alcoholic Fatty Liver in Rats | Journal of Life Science |
|
|
|||
| Kim BH10 | 2018 | The Effects of Injinsaryung-san on Rat with Alcoholic Fatty Liver | Herbal formula science |
|
|
|||
| Kim BH11 | 2018 | The Effects of Scutellaria Radix Extract on the Alcohol-Induced Fatty Acid Synthesis of Liver in Rats | J Korean Med Obes Res |
|
|
|||
| Kim TR12 | 2017 | A Case Report of Alcoholic Liver Disease with Lower Limb Weakness | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Kang KW13 | 2016 | A Case of Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis Treated with Injinoryeong-san | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Jeong YE14 | 2016 | A Case Report of Patient with Acute Alcoholic Hepatitis and Renal Dysfunction | J Korean Med Obes Res |
|
|
|||
| Kim EH15 | 2016 | Protective effects of Cirsium setidens ethanolic extracts against alcoholic fatty liver injury in rats | J Nutr Health |
|
|
|||
| Han MK16 | 2015 | The Clinical Report of Flank Pain Induced by Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis with Soshihotang-gamibang | The Journal of East-West Medicine |
|
|
|||
| Kim JY17 | 2014 | Protective Effect of Citrus unshiu Peel Extract on Ethanol- Induced Fatty Liver in Rats | J Korean Soc Food SciNutr |
|
|
|||
| Baik TH18 | 2012 | Non-traumatic Spontaneous Gastrocnemius Muscle Blood Stasis Associated with Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis | Korean J Oriental Physiology & Pathology |
|
|
|||
| Rho EJ19 | 2011 | A Clinical Report of Chronic Alcoholic Liver Disease treated by Zhizihoupo Tang | J of KMediACS |
|
|
|||
| Kim J20 | 2010 | A Case Report of ascites in Liver cirrhosis treated with Saenggangeonbi-tang | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Kim JJ21 | 2010 | Preventive Effects of Daekumeumja on Fatty Degeneration of Liver and Immunosuppression Induced by Alcohol | Korean journal of oriental medicine |
|
|
|||
| Kim HY22 | 2009 | A Clinical Report on 1 case of the Jaundice Caused by the Alcoholic Liver Disease | The Journal of East-West Medicine |
|
|
|||
| Kim JE23 | 2009 | A Study of Syndrome Differentiation Types of Alcoholic Liver Disease | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Choi GY24 | 2009 | Case Report of Ascites in Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis | Korean J Oriental Physiology & Pathology |
|
|
|||
| Shin YJ25 | 2009 | Clinical study of Alcoholic Liver Disease Treated with Sodalgeonbi-tang | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Kim JE26 | 2009 | Study to Develop the Pattern Identification Questionnaire for Alcoholic Hepatitis | Korean J Oriental Physiology & Pathology |
|
|
|||
| Shin YS27 | 2008 | A Clinical Report of Ascites Induced by Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis with Saenggangeonbi-tang | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Hong SH28 | 2008 | Effects of Injinoryung-San on Alcoholic Hepatitis | Korean J Oriental Physiology & Pathology |
|
|
|||
| Choi SH29 | 2008 | Two Cases report of Chunggan plus (Gamichunggan-tang) for Hepatitic C patient and Alcoholic Hepatitis patient with Cerebral-infarction | Herbal formula science |
|
|
|||
| Jeong EW30 | 2007 | Chunggangunbi-tang-gamibang’s Effect on Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis with Ascites | Herbal formula science |
|
|
|||
| Zheng CX31 | 2004 | The Effects of Ka-Mi-Chung-Gan-Tang on Rat with Alcoholic Fatty Liver | Kor K Parmacogn |
|
|
|||
| Lee TH32 | 2003 | A case of Intracerebral Hemorhage with Alcoholic liver disease | Journal of Pharmacopuncture |
|
|
|||
| Lee JH33 | 2001 | A Clinical Study of the Effects of Chungganhaeju-tang on Alcoholic Fatty Liver | J Korean Oriental Med |
|
|
|||
| Lee YY34 | 2001 | The Clinical Report about Patients with Alcoholic Liver Disease given Gamichunggan-san | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Cheon YS35 | 2001 | The effects of Injinsugunomija Extract on Liver Function Test of Alcoholic Liver Disease and Viral Hepatitis Patients | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Yeo EK36 | 2000 | A Alcoholic Liver Disease Patient Case with Diabetes Mellitus | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Lee E37 | 2000 | Saenggangeonbi-tang’s Effect on Alcoholic Liver Cirrhosis - 1 case | J Korean Oriental Med |
|
|
|||
| Han SS38 | 2000 | The study on Oriental and Western medical of Liver cirrhosis (Fibrosis) pathological system | Journal of Hawhwa Medicine |
|
|
|||
| Ko H39 | 1999 | Alcoholic Liver disease complicated with ascites in three patients using a herbal medicine (CheungganHaeju-tang) | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Hong SH5 | 1999 | Clinical report and study on Alcoholic Liver Disease | The journal of Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Society |
|
|
|||
| Kim JD40 | 1996 | The study on Oriental and Western medical of Alcoholic Liver Disease | J Int Korean Med |
|
|
|||
| Yoon SH41 | 1993 | Response of Kagamseanggantang on the Liver Function in Alcoholic Liver Diseases | J Korean Oriental Med |
2. 실험연구
총 8편의 실험연구 모두가 In vivo 실험연구에 해당하였다. 모두 Sprague-Dawley rats를 대상으로 하여 ALD에서 한약재제의 효과를 실험하였으며, 약물은 모두 경구로 투약되었다. 투여 기간은 3일에서 8주까지 다양하나 8주 동안 투여한 논문이 가장 많았다 4편에서 단일본초로 황금 추출물, 고초균발효누에 추출물, 곤드레 추출물, 진피 추출물이 각각 사용되었고, 1편에서는 오미자, 인진호, 알로에베라 추출물 혼합물을 이용하였으며, 3편에서 인진사령산 추출물, 대금음자 추출물, 가미청간탕 추출물을 사용하였다. 2개의 논문8,15에서 본 실험 이전에 알코올성 간질환을 유도한 쥐를 이용하였고, 6편의 논문에서는 추출물과 에탄올을 함께 투여하여 에탄올만 투여한 대조군과 비교하였다.
김 등의 연구8에서는 오미자, 인진, 노회 추출물 혼합이 alanine aminotransferase(ALT), gamma glutamyl transferase(GGT) 등의 간 기능 지표 효소 활성과 지질과산화물 수준을 감소시키며, 항산화 효소 활성 증가와 glutathione(GSH) 함량 감소 억제 등을 통해 알코올성 지방간 개선에 효과적임을 밝혔다. 김 등의 연구9에서는 고초균발효누에추출물이 혈중 간 기능 지표 수준 개선, 간 조직 및 혈중 중성지질과 조직 내 과산화지질 농도 개선 등의 효과를 보여 알코올성 간 손상에 대한 개선효과를 밝혔다. 김의 연구10에서는 인진사령산이 알코올 섭취로 인한 tumor necrosis factor-alpha(TNF-α)의 증가를 억제하는 것을 밝혔다. 김의 연구11에서는 실험을 통해 인진사령산 추출물이 간세포에서의 TNF-α의 발현을 억제하여 알코올 투여로 인한 간의 무게 감소와 ALT, asparatate aminotransferase(AST)의 상승을 억제시키고 지방방울의 형성, 지방변성 같은 병리적 변화를 감소시키는 것을 밝혔다. 김 등15은 곤드레가 알코올에 의한 간 손상 및 지방간 발생을 억제함을 확인하였으며 이 과정에서 nuclear factor kappa B(NFκB) 활성 억제와 AMP activated protein kinase(AMPK) 활성 증가가 관여함을 제시하였다. 김 등17은 진피 추출물 속의 다양한 플라보노이드 성분이 알코올 섭취로 인한 간 기능 지표 수준을 개선시키고, 간조직에서 지방간 형성을 유의하게 억제시켜 지방간 증상을 완화시킬 수 있음을 증명하였다. 김 등21은 대금음자가 ethanol로 유발된 간 지방병증과 면역저하를 용량 의존적으로 억제함을 밝혔다. 정 등31은 가미청간탕이 에탄올에 의한 지방간 생성과 malondialdehyde(MDA) 함량 증가, GSH 함량 저하를 억제하는 효과가 있다는 것을 실험으로 보여주었다(Table 2).
Table 2
In Vivo Studies About Alcoholic Liver Disease on Traditional Medicine
| Author (year) | Animal | Medication | Route & period | Results | Herbal composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim8 (2018) | Sprague-Dawley Rats administered chronic ethanol-induced fatty liver model (n=48) | mixing extracts of S. chinensis, A. capillaris, Aloe vera (SAL5) | Oral, 5 weeks |
①decreased liver marker enzymes activities of ALT, GGT in serum and TG activities in liver. ②SAL5 increased the level of GSH and the activities of CAT, SOD ③ SAL5 delayed the development of an alcoholic fatty liver by reversing fat accumulation in the liver, as evidenced in histological observations. ④ The gene expression of mRNA were decreased at the IL-1β, NOS-II, TNF-α and MMP-2 by SAL5. |
S. chinensis extract, A. capillaris extract, Aloe vera=4 : 8 : 3 |
|
|
|||||
| Kim9 (2018) | Sprague-Dawley rat (n=42) | extracts from Bacillus subtilis-fermented Bombyxmori L. + ethanol | Oral, 4 weeks |
①The triglyceride concentrations in the liver and serum and The activities of ALT, AST, ALP, and LDH in the serum were reduced in the BSP5 group. ②the contents of free fatty acids, total lipids, and total cholesterol were reduced in the BSP5. ③ The activities of ADH, ALDH and ADH, ALDH protein levels in the liver were increased in the BSP5 group. ④ BSP5 treatment prevented alcohol -induced lipid droplet accumulation in the hepatocytes. |
Bacillus subtilis-fermented Bombyxmori L. |
|
|
|||||
| Kim10 (2018) | Sprague-Dawley Rat (n=30) | Injinsaryung-san extract + Ethanol | Oral (1회/day), 8 weeks |
①Injinsaryung-san extract inhibited AST, AST value increase. ②Histopathological changes were reduced and the expression of TNF-α was markedly attenuated |
Artemisia capillaris Thunberg 50 g, Alismaorientale Juzepzuk 24 g, Atractylodesmacrocephala Koidzumi, Poriacocos Wolf, Polyporusumbellatus Fries 각 12 g |
|
|
|||||
| Kim11 (2018) | Sprague-Dawley Rat (n=30) | Scutellaria Radix extract + Ethanol | Oral (1회/day), 8 weeks |
①Scutellaria Radix extract inhibited AST, AST value increase. ②Histopathological changes as ballooning, fatty and hydropic degeneration were reduced ③ the expression of TNF-α was markedly attenuated |
Scutellaria Radix |
|
|
|||||
| Kim15 (2016) | Sprague-Dawley rats fed ethanol (35.5% of total calories) liquid diet (n=28) | Cirsium setidens ethanolic extract (CS) | Oral, 8 weeks |
①CS suppressed alcohol-induced lipid droplets accumulation in the liver tissues ②CS inhibited alcohol-induced increases in activities of ALT and AST ③ CS reduced hepatic and serum TG concentrations ④ CS supplementation increased hepatic levels of p-ACC and p-AMPK and inhibited alcoholinduced phosphorylation of NFκB, which was associated with reduced hepatic protein levels of TNFα. |
Cirsium setidens |
|
|
|||||
| Kim17 (2014) | Sprague-Dawley rat (n=42) | Citrus unshiu peel extract (CPE) + Lieber-Decarli ethanol diet | Oral, 6 weeks |
①CPE administration improved fat accumulation in livers, which was inducedby ethanol diet. ②Serum levels of lipids and transaminases were reduced by CPE consumption. |
Citrus unshiu |
|
|
|||||
| Kim21 (2010) | Sprague-Dawley Rat (n=40) | Daekumeumja + 25% alcohol | Oral (1회/day), 8 weeks |
①significant decrease of LFT value and increase of relative body weights of liver, thymus and spleen ②significant decrease of numbers of hepatocytes and percentages of regions occupied by lipid droplets ③ significant increase of lobular thickness and cortex thickness, splenic thicknesses, numbers of white pulps and mean diameters of white pulps ④ effective inhibition of severe fatty changes and atrophic changes in thymus and spleen |
CitriPericarpium 12.0 g, Magnoliae Cortex, Atractylodis Rhizoma, glycyrrhizae Radix 각 2.8 g |
|
|
|||||
| Zheng31 (2004) | Sprague-Dawley rats administered ethanol-induced fatty liver model (n=not reported) | Ka-Mi-Chung-Gan-Tang (KMCGT) | Oral, 3 days | KMCGT ignited significantly the increase of triglyceride, cholesterol and lipid peroxidation in liver tissues. the activities of GOT, GPT |
Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer, Bupleurumfalcatum, Scutellariabaicalensis, Pinelliaternata Breitenbach, Artemisia capillaris Thunb, Gardenia radicans Thunb, Zingiberofficinale Rosc, Zizyphusjujuba, Glycyrrhizaglabra L. |
3. 임상연구
임상연구 논문은 총 26편으로 그 중 case report 17편(65.4%), case series 7편(26.9%), assessment scale(평가척도연구) 1편(3.8%), 무작위대조시험(Randomized controlled trial, RCT) 1편(3.8%)으로 논문의 대다수가 증례보고에 그쳤다(Table 3).
Table 3
Clinical Research about Alcoholic Liver Disease
| Author (year) | Sample size | Treatment period | Intervention | result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case report | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Jeong6 (2018) | M/73 (n=1) | 13 days | herbal decoction (Palmijihwang-hwan), herbal extracts (Oryung-san), acupuncture (LU8, KI7, SP3, KI3, HT7), moxibustion (CV12, CV4), cupping (back shu point) | clinical symptoms were improved | |
|
|
|||||
| Kim12 (2017) | M/72 (n=1) | 29 days | acupuncture (SP4, SP6, ST36, GB8, LI4, GV20), moxibustion (CV12), herbal decoction (Bangpungtongsungsan, InjinBunrieum, Gamijihwang-tang, Yukmijihwangtang-gamibang) | lower limb weaknessand abdominal discomfort were improved. the LFT valuewas decreased | |
|
|
|||||
| Kang13 (2016) | M/37 (n=1) | 14 days | herbal decoction (Injinoryeong-san), acupuncture (LR1, LR2, LR3, LR4, LR8), moxibustion (CV12) | clinical symptomswere improved and decreased in abdominal circumference and body weight. Laboratory results also improved, and the ChildPugh score increased from class B to A. | |
|
|
|||||
| Jeong14 (2016) | M/57 (n=1) | 31 days | herbal decoction (Galhwahajung-tang, Yijintang-gamibang), acupuncture (CV12, LU8, HT8, LR2, LR4, PC6, LR1, SP1, SP2, SP3, K10), pharmacopuncture (SBV 0.3 ml CV12, ST36 / Hominisplacent 0.4 ml LU4, BL57), moxibustion (CV12, CV0), cupping (back shu point) | clinical symptoms were improved the LFT & RFT value (AST, ALT, GGT, creatine) was decreased. | |
|
|
|||||
| Han16 (2015) | M/34 (n=1) | 6 days | herbal decoction (Soshihotang-gamibang), acupuncture (G41, B66, TE2, TE3, GB34, TE6, SP3, K10), moxibustion (CV12, CV0), cupping (back shu point), pharmacopuncture (Hominisplacent 1 cc) | Right flank pain were improved (VAS 7→1, Pain Frequency 10→2) | |
|
|
|||||
| Baik18 (2012) | M/50 (n=1) | 98 days | electroacupuncture, pharmacopuncture (SBV), moxibustion | Spontaneous gastrocnemius muscle blood stasis was reduced. | |
|
|
|||||
| Rho19 (2011) | M/50 (n=1) | 4 months | herbal decoction (ZhizihoupoTang) | clinical symptomswere improved the LFT valuewas decreased | |
|
|
|||||
| Kim20 (2010) | F/69 (n=1) | 117 days | herbal decoction (Saenggangeonbi-tang), acupuncture (LI4, LR3, ST36, TE3, GB41, GV20), moxibustion (CV12) | the ascites has disappeared on the ultrasonography. | |
|
|
|||||
| Kim22 (2009) | F/42 (n=1) | 7 days | herbal decoction (Ondam-tang, Yukul-tang, Soyo-san), acupuncture | clinical symptomswere improved the LFT valuewas decreased | |
|
|
|||||
| Choi24 (2009) | M/71 (n=1) | 4 weeks | herbal medication (Daekumeumja extracts), acupuncture (PC3, LU9, TE3, GB34, BL60, LR3, GB14, CV12, CV6), moxibustion (CV12) | Reduction of ascites is proved by abdominal CT & US lab findings of liver functionshowed improvement | |
|
|
|||||
| Shin27 (2008) | M/50 (n=1) | 2 months | herbal medication (Saenggangeonbi-tang, Oryung-sanhapBojungikki-tang extracts), acupuncture (LI4, LR3, ST36, SP6, PC6), moxibustion (CV12, CV4, CV8) | remarkable effect on clinical symtomsand lap findings (AST, ALT, γ-GTP, ALP). | |
|
|
|||||
| Choi29 (2008) | M/71 (n=1) | 24 days | herbal medication (Chunggan plus Viscous Extracts (Gamichunggan-tang), oohwangchungsim-won), acupuncture (LU5, LI4, SP10, SP6, ST8, BL1, CV13, CV12) | the level of AST, ALT, GGT was significantly normalized. | |
|
|
|||||
| Jeong30 (2007) | M/64 (n=1) | 77 days | herbal decoction (Chunggangunbi-tang-gamibang), acupuncture (GV20, GB7, GB21, GB31, ST36, LI11, GB39, CV12, ST36, LI4, LR3, SP1, SP2, HT8, LR1), moxibustion (CV12, CV8, CV4), cupping (back shu point) | remarkable effects on clinical symptoms (dizziness, abdominal discomfort, itching, diarrhea), blood test results, and abdomen ultrasonographic images | |
|
|
|||||
| Lee32 (2003) | M/62 (n=1) | 2 months | herbal decoction (administrated Taeumjowetang), acupuncture (GV20, GB20, LI11, TE5, LI4, GB31, GB39, ST36, GB41, LR3, LR4, LR2, CV12, ST25), pharmacopuncture (GV20, GB7, GB21, GB31, ST36, LI11, GB39 CFC 20 cc) | clinical symptoms (chest discomfort, abdominal discomfort) and liver function (AST, ALT, GGT, ALP, TG) were prominently improved. | |
|
|
|||||
| Yeo36 (2000) | M/40 (n=1) | not reported | herbal decoction (Gamijihwangtang, Saenggangeonbi-tang) | clinical symptom, blood sugar and liver function (GGT, Total cholesterol, TG) were improved for 3 times of treatment. | |
|
|
|||||
| Lee37 (2000) | M/53 (n=1) | 20 days | herbal decoction (Saenggangeonbi-tang) | all the main symptoms disappeared and the patient’s nutritional state was improved. Child Pugh’s grade has changed form B to A. | |
|
|
|||||
| Hong5 (1999) | M/39 (n=1) | 13 days | acupuncture (GV20, CV17, CV12, LI11, ST36, LR14, GB34, BL17, BL18, BL19) | Clinical symptoms, LFT level were improved. | |
|
|
|||||
| Case series | |||||
| Bae7 (2018) | ①M/67 ②M/66 | ①169 days ②78 days | herbal decoction (Chungganhaeju-tang), auricularacupuncture (TF4, CO12, CO11, AT4, AT2) | ①no improvements ②clinical symptomsand laboratory testswere markedly improved | |
|
|
|||||
| Shin25 (2009) | ①F/78 ②M/27 ③ M/38 ④ M/32 ⑤ M/43 | 7-10 days | herbal decoction (Sodalgeonbi-tang) | AST, ALT, GGT were reduced and incidental symptoms such as fatigue, nausea and indigestion were improved. | |
|
|
|||||
| Lee33 (2001) | n=30 | 1 month | herbal decoction (Chungganhaeju-tang) | Chungganhaeju-tang has effects on the improvement of clinical symptomsand LFT levels were decreased (P<0.05) | |
|
|
|||||
| Lee34 (2001) | n=25 | over 1 month | herbal decoction (Gamichunggan-san) | Effect on the improvement of clinical symptoms and the improvement ratio of AST, ALT, GGT was 77.8%, 61.5%, 76.2%. All of the patients with alcoholic hepatitis with the inverted ratio of lymphocytes was improved. | |
|
|
|||||
| Cheon35 (2001) | n=10 | 1 month | herbal medication (Injinsugunomija extract) | 70% of ALD patients’ LFT values have improved by Injinsugunomija extract (3 cases improve prominent and 4 cases improve effective and 3 cases are ineffective) | |
|
|
|||||
| Ko39 (1999) | ①M/52 ②M/60 ③ M/48 | ①2 months ②2 months ③ 2 weeks | herbal decoction (CheungganHaeju-tang) | clinical symptoms, LFT value were improved. | |
|
|
|||||
| Yoon41 (1993) | n=10 | 37.2±7.4 days | herbal decoction (Kagamseanggantang) | Elevated liver function of all these subjects were returned within normal limit | |
|
|
|||||
| Assessment scale study | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Kim26 (2009) | n=79 | - | - (n=36) | - (n=43) | the questionnaire would be effective instruments of pattern identification for alcoholic hepatitis (Cronbach alpha=0.7) |
|
|
|||||
| Randomized clinical trial | |||||
|
|
|||||
| Hong28 (2008) | n=27 | 6 weeks | herbal medication (Injinoryung-San extract), alcohol abstinence (n=15) | alcohol abstinence (n=12) | Injinoryung-San has pharmaceutical efficacy only in GGT, MCV on liver injury patients induced by alcohol. |
평가척도연구 1편26은 알코올성 간염의 변증설문을 고안하여 그 유효성을 실험한 것으로 알코올성 간염 군과 정상군에게 변증설문을 적용하여 비교하였을 때 Cronbach Coefficient Alpha 값이 0.7 이상으로 설문지의 신뢰도가 확보되었으며 肝, 濕, 熱의 변증 설문 문항이 알코올성 간염군에서 유의성 있게 의미 있음을 밝힌 연구였다.
1편의 RCT 논문28은 알코올성 간염 환자 군에게 인진오령산엑기스제제를 6주간 투여하였을 때 대조군인 6주간 단순 금주한 환자군과 비교한 연구로 GGT와 mean corpuscular volume(MCV)의 경우 대조군에 비해 유의하게 감소하였으나 AST, ALT에서는 유의하지 않았다.
임상연구 논문 26편에서 대상자는 총 183명이었으며 그 중 평균 나이만을 제시하였거나 나이를 언급하지 않은 논문 6편26,28,33-35,41을 제외하였을 때 연구에서 평균나이는 53.5세, 최저나이는 27세, 최고나이는 78세로 나타났다. 대상자 27명 중 50, 60대가 각각 22.2%로 가장 많았다. 대상자의 성별을 언급하지 않은 논문26,28,33,35을 제외한 21편의 논문에서 남성 50명(94.3%), 여성 3명(5.7%)으로 남성의 비율이 더 높았다.
임상 논문에서 언급된 증상을 살펴 보면 피로가 48명으로 가장 자주 호소하였고 식욕부진이 27명, 소화불량이 25명으로 그 다음이었다. Table 4에 각 논문에서 다빈도로 언급되는 9가지 증상을 정리하였다. 연구대상이 1명인 증례보고에서 증상이 언급된 경우 ‘O’로 표기하였으며 연구대상이 2명 이상인 연구에서는 언급된 사람 수를 표기하였다. 표에 언급된 9가지 증상 외에도 협통, 마목, 진전, 두통, 무력감, 복부팽만감 등이 자주 제시되었다.
Table 4
Clinical Symptoms of Alcoholic Liver Disease
| Author (year) | Clinical symptoms | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatigue | Anorexia | Dyspepsia | Insomnia | Nausea | Ascites | Abdominal discomfort | Dizziness | Abdominal pain | |
| Jeong6 | O | O | |||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Kim12 | O | ||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Kang13 | O | O | |||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Jeong14 | O | O | |||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Rho19 | O | O | |||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Kim20 | O | ||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Kim22 | O | O | O | O | |||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Choi24 | O | O | O | O | |||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Shin27 | O | O | |||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Choi29 | O | O | O | ||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Jeong30 | O | O | O | O | |||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Lee32 | O | O | O | ||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Yeo36 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |||
|
|
|||||||||
| Lee37 | O | O | O | O | O | O | |||
|
|
|||||||||
| Hong5 | O | O | O | ||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Bae7 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Shin25 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | |||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Lee133 | 23 | 15 | 11 | 3 | 2 | ||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Lee234 | 10 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
|
|
|||||||||
| Ko39 | O | O | O | O | |||||
|
|
|||||||||
| Total | 48 | 27 | 25 | 11 | 11 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 |
임상연구 26편중 14편의 논문에서 변증을 언급하였다. 한 논문에서 2가지 이상의 변증을 언급한 경우를 별개로 분류하였을 때 9편에서(64.3%) ALD를 濕熱로, 특히 肝膽濕熱(6편)로 변증하여 치료하였다. 그 외에도 腎陰不足, 氣滯 등이 있었다(Table 5).
Table 5
The Pattern Identification of Alcoholic Liver Disease
| Frequency | Pattern identification |
|---|---|
| 9 | 濕熱 (肝膽濕熱, 肝經濕熱, 脾胃濕熱, 濕熱內鬱)12-14,22,27,28,36,37 |
|
|
|
| 4 | 腎陰不足 (肝腎陰虛, 腎虛)5,6,12,36 |
|
|
|
| 3 | 氣滯 (氣滯瘀血, 氣滯濕阻, 氣血鬱滯)18,24,30 |
|
|
|
| 1 | 痰濕壅滯6, 脾肺鬱熱28, 死血脇痛16 |
임상연구의 중재로는 한약이 가장 자주 쓰였으며 침, 약침, 뜸, 부항 등이 사용되었다. 임상연구 논문 26편 중 3편을 제외한 23편(88.5%)의 논문에서 한약을 치료 중재로 사용하였다. 한 논문에서 2가지 이상의 처방을 사용한 경우 별개로 분류하였고 동일 처방에서 가감한 경우 동일 처방으로 보고 처방을 정리하였다(Table 6). 사용된 한약 처방은 총 23가지이며 生肝健脾湯이 4편, 淸肝解酒湯이 3편에서 사용되어 가장 자주 쓰였다. 23가지 처방에서 2회 이상 사용된 약재를 표로 정리하였다(Table 7). 茯苓이 19회로 가장 자주 사용되었는데, 白茯苓이 12회, 赤茯苓이 4회, 둘을 구분하지 않고 茯苓으로 표기된 경우가 3회였다. 그 다음으로 澤瀉가 14회, 甘草, 白朮, 茵蔯이 각각 13회로 다용되었다.
Table 6
List of Herbal Medication in Clinical Treatments of Study Case
| Frequency | Herb medication |
|---|---|
| 4 | 生肝健脾湯 |
|
|
|
| 3 | 淸肝解酒湯 |
|
|
|
| 2 | 五苓散 |
|
|
|
| 1 | 茵蔯五笭散, 地黃湯, 淸肝散, 葛花解醒湯, 對金飮子, 防風通聖散, 生肝湯, 消疸健脾湯, 小柴胡湯, 逍遙散, 溫膽湯, 牛黃淸心元, 六味地黃湯, 六鬱湯, 二陳湯, 茵蔯分利飮, 淸肝健脾湯, 梔子豉湯, 太陰調胃湯, 八味地黃丸 |
침치료를 치료 중재로 사용한 15편의 논문 중에서 사용한 혈위가 기재되지 않은 논문 2편을 제외하고 사용된 혈위 처방을 정리하였다(Table 8). 개별 혈위 중 가장 자주 쓰인 자리는 中脘(CV12), 合谷(LI4), 太衝(LR3), 足三里(ST36)이었다. 약침을 치료 중재로 사용한 논문은 3편이었으며 1편에서 전침을 병용하였다.
Table 7
List of Herb Name
Table 8
List of Acupoints in Clinical Treatments
ALD의 치료 효과를 평가하기 위해 임상 증상의 호전 정도를 기재한 20편의 논문에서 9가지 다빈도 임상 증상을 표로 정리하였다(Table 9). 치료 후 증상에 변화에 대해 언급이 없는 경우 Unclear로 표시하였고 증상이 소실되었을 경우 Loss로 표기하였다. 각 논문에서 증상의 호전도를 표현한 방법은 경과를 글로 서술한 경우와 증상의 강도를 기호로 나타내는 것으로 나눌 수 있다. 대부분의 논문에서 호전도를 경과에 따라 글로 서술하였으며 전체 논문 중 9편5,7,19,22,25,30,32,37,39에서 증상의 강도를 +++(Severe), ++(moderate), +(slight or mild), ±(trace), -(non-existed or loss)으로 나누어 표현하였다. 여의 연구36에서 복부불편감의 호전이 없었던 것을 제외하고 대부분의 논문들에서 치료 종료 후 증상들이 mild 혹은 loss로 호전되었다. 그 외에도 여러 가지 평가 척도를 이용하여 호전 정도를 나타내기도 하였는데 복통이나 협통 같은 통증의 경우 Visual Analogue Scale(VAS)을 사용13,14,16,18,24한 연구가 많았다. 신 등27은 부종의 호전을 나타내기 위해 체성분 검사의 부종지수를 사용하였는데 치료 전 +0.385에서 치료 후 +0.359로 감소하였다. 근력저하의 호전은 평가척도인 Manual Muscle Test(MMT), National Institute of Health Stroke Scale(NIHSS), Hughes grading scale을 이용하였는데 김 등의 연구12에서는 치료 후 MMT 3-4에서 4-5로, Hughes grading scale 2에서 1로 근력의 호전을 보였다. Choi 등의 연구29에서는 MMT 3에서 4로, NIHSS 2에서 1로 근력의 증가를 평가하였으며, Lee 등의 연구32에서는 MMT 우측0, 좌측2에서 우측 3, 좌측 4로의 호전을 보였다. 복수의 경우 영상학적 자료로 증상의 호전을 객관적으로 평가한 경우가 많았는데 김 등의 연구20에서는 치료 전 복부 전산화 단층촬영(computed tomography, CT)과 초음파 영상에서 확인한 1000 cc정도의 복수가 치료 후 시행한 초음파 영상에서 모두 소실되었음을 확인하였다. 최 등24은 치료 전 복부 CT와 초음파 영상에서 보였던 복수가 치료 후 거의 소실 됨을 영상 자료를 통해 확인하였으며 정의 연구30에서는 초음파 영상을 통해 치료 후 복수가 25% 감소됨을 보고하였다. 또한 강 등15과 이 등37의 연구에서는 Child-pugh score를 사용하였는데 두 연구에서 모두 Child-pugh grade가 B인 환자가 치료 후에 A로 호전되었다.
Table 9
Clinical Progress
| Author (year) | Case | Clinical symptoms | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||||
| Fatigue | Anorexia | Dyspepsia | Insomnia | Nausea | Ascites | Abdominal discomfort | Dizziness | Abdominal pain | ||
| Jeong6 | 80%↓ | loss | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Kim12 | improved | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Kang13 | near normal | VAS10→5 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Jeong14 | unclear | VAS7→2 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Rho19 | +++→- | +++→- | +++→- | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Kim20 | 1000 cc→loss | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Kim22 | +++→+ | +++→+ | 2-3 hrs→ 4-5 hrs | +→- | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Choi24 | improved | almost loss | improved | improved | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Shin27 | improved | Edema Index+0.385 →+0.359 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Choi29 | unclear | improved | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Jeong30 | ++→± | ++→- | 25%↓ | ++→- | ++→± | |||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Lee32 | +++→+ | +++→- | +++→- | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Yeo36 | ① | unclear | improved | improved | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| ② | improved | improved | improved | no change | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| ③ | improved | improved | improved | loss | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Lee37 | ++→- | ++→+ | +++→± | insomnia→deep sleep | ++→- | +++→+ | ++→- | |||
|
|
||||||||||
| Hong5 | ++→- | +→- | +→- | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Bae7 | ① | +→± | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| ② | +→- | ++→- | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Shin25 | ① | +++→+ | ++→- | ++→- | ++→+ | |||||
|
|
||||||||||
| ② | ++→+ | +→- | +→- | ++→+ | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| ③ | ++→- | +→- | +→- | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| ④ | ++→- | +→- | ++→- | +→- | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| ⑤ | ++→+ | +→- | ++→- | +→+ | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||
| Ko39 | +→- | +→- | +→- | +→- | ||||||
객관적으로 치료 효과를 평가하기 위해 2편의 논문16,26을 제외한 모든 논문에서 간기능 검사(Liver Function Test, LFT)를 시행하였는데 이러한 LFT 수치 변화를 표로 정리하였다(Table 10). LFT는 기계마다 각 항목의 단위나 정상범위가 조금씩 다를 수 있으며 각 연구 별 호전 정도를 명확하게 구분하기 위해 변화된 정도를 백분율로 표시하였다. Case Series나 RCT 논문에서는 치료 전후의 LFT 평균 수치의 비율을 구하였다. 치료 시작 시점과 가장 가까운 LFT 검사 일자와 치료 종료 후 혹은 치료 중 가장 마지막 LFT 검사 일자까지의 기간도 표기하였다. 윤의 연구41의 경우 LFT의 수치가 정상이 되는 기간만 기록하고 검사 수치가 나와 있지 않아 제외하였다. 3편7,20,36을 제외한 연구에서 측정한 모든 LFT 수치가 호전되었다. 그 중에서도 모든 수치가 정상 범위로 호전된 경우는 6편5,6,12,14,25,33이 있었으며 가장 큰 수치의 변화를 나타낸 경우는 이의 연구32로 17일 만에 AST가 92.9%, ALT가 81.9%, Total Bilirubin이 80%씩 감소하면서 정상 범위로 회복하였다. 정상 범위로 회복되지 못한 경우가 가장 많은 항목은 GGT(69.2%)이었으며 그 다음 alkaline phosphatase(ALP)(38.4%), Total Bilirubin(37.5%) 순이었다.
Table 10
Effects of Korean Traditional Medicine on Liver Functional Test
| Author | case | Period | AST | ALT | GGT | ALP | Total Bilirubin | Direct Bilirubin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jeong6 | 11 | 65.6%↓ | 58.8%↓ | 47.3%↓ | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Kim12 | 26 | 84.4%↓ | 80.4%↓ | 59.3%↓ | 78.9%↓ | |||
|
|
||||||||
| Kang13 | 10 | 77.5%↓ | 69.6%↓ | 51.8%↓ | 53.1%↓ | 73.1%↓ | 82.1%↓ | |
|
|
||||||||
| Jeong14 | 29 | 68.8%↓ | 82.9%↓ | 60.4%↓ | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Baik18 | 29 | 86.9%↓ | 73.3%↓ | 27.3%↓ | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Rho19 | 54 | 86.3%↓ | 89.0%↓ | 34.6%↓ | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Kim20 | 112 | 29.6%↓ | 47.0%↓ | 71.9%↑ | 30%↓ | |||
|
|
||||||||
| Kim22 | 2 | 5%↓ | 2.9%↓ | 1.7%↓ | 37.5%↓ | |||
|
|
||||||||
| Choi24 | 27 | 70.4%↓ | 60.9%↓ | 71%↓ | 24.2%↓ | 59.7%↓ | ||
|
|
||||||||
| Shin27 | 54 | 68.1%↓ | 11.5%↓ | 81.4%↓ | 69.7%↓ | 80%↓ | ||
|
|
||||||||
| Choi29 | 17 | 61.6%↓ | 34.5%↓ | 66%↓ | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Jeong30 | 76 | 27.0%↓ | 12.5%↓ | 44.8%↓ | 24.3%↓ | 32.7%↓ | 61.2%↓ | |
|
|
||||||||
| Lee32 | 17 | 92.9%↓ | 81.9%↓ | 72.6%↓ | 68.5%↓ | 80%↓ | ||
|
|
||||||||
| Yeo36 | ① | 8 | 25%↑ | 21.2%↓ | 8.3%↓ | 11.1%↑ | 2fold↑ | |
|
|
||||||||
| ② | 16 | 50.6%↓ | 29.6%↑ | 2.6%↑ | 57.1%↓ | 50%↓ | ||
|
|
||||||||
| ③ | 6 | 13.0%↓ | 3fold↑ | 27.5%↓ | 62.5%↓ | 40%↓ | ||
|
|
||||||||
| Lee37 | 30 | 77.1%↓ | 47.1%↓ | 66.1%↓ | 48.1%↓ | |||
|
|
||||||||
| Hong5 | 73 | 18.2%↓ | 22.9%↓ | 79.6%↓ | 22.2%↓ | |||
|
|
||||||||
| Bae7 | ① | 154 | 25.6%↓ | 37.9%↓ | 13.1%↓ | 20.3%↓ | 4.2%↓ | |
|
|
||||||||
| ② | 77 | 56.7%↓ | 45.7%↑ | 85.8%↓ | 44%↓ | |||
|
|
||||||||
| Shin25 | ① | 19 | 83.1%↓ | 56%↓ | 20.3%↓ | |||
|
|
||||||||
| ② | 9 | 16.7%↓ | 29%↓ | |||||
|
|
||||||||
| ③ | 12 | 68.8%↓ | 68.1%↓ | |||||
|
|
||||||||
| ④ | 7 | 57.6%↓ | 51.7%↓ | |||||
|
|
||||||||
| ⑤ | 21 | 7.4%↓ | 44.9%↓ | 40.9%↓ | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Lee133 | 30 | 37.5%↓ | 27.1%↓ | 39.3%↓ | ||||
|
|
||||||||
| Lee234 | not reported | 49.5%↓ | 29.3%↓ | 51.7%↓ | 23.1%↓ | 57.7%↓ | 36.7%↓ | |
|
|
||||||||
| Cheon35 | 30 | 36.3%↓ | 39.1%↓ | 47.1%↓ | 0.4%↓ | 27.3%↓ | ||
|
|
||||||||
| Ko39 | 47 | 66.7%↓ | 2.7%↓ | 64.2%↓ | 35.6%↓ | 21.7%↓ | ||
| Hong28 | E* | 42 | 82.0%↓ | 85.5%↓ | 44.0%↓ | |||
|
|
||||||||
| C† | 42 | 71.2%↓ | 76.3%↓ | 55.8%↓ | ||||
IV. 고찰 및 결론
ALD 발병 기전은 아직 완전하게 이해되지는 않았으나 행동적, 환경적, 유전적 요인 사이의 상호 작용이 관련되어있는 것으로 본다. ALD의 조직학적 특징은 지속적인 알코올 노출의 맥락에서 상호 관련되고 연속적인 병태생리학적 결과로 볼 수 있다. 에탄올은 간세포 내에서 알코올탈수소효소, cytochrome P450 2E1(CYP2E1), 카탈라아제에 의해 아세트알데히드로 대사된다. 아세트알데히드는 강한 독성 및 돌연변이 성 알코올 대사산물이며 CYP2E1는 이러한 아세트알데히드의 생성에 관여할 뿐만 아니라 활성산소의 형성에 의한 산화적 손상을 일으킨다2. 에탄올 대사로 인해 활성산소가 생성되고 지질의 과산화반응과 GSH, S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine 등 대사물질들이 간세포를 손상에 민감하게 만든다. 또한 아세트알데히드는 초산으로 대사되는데 이것이 단백질과 DNA에 결합하여 기능을 변화시키고 단백질 형성에도 영향을 미친다. 이렇게 알코올 대사로 인해 생성된 물질들은 면역체계를 활성화시키는 자가 항원으로 작용하여 간 손상을 일으키기도 하며 신호경로를 자극하여 TNF-α, IL-17 등의 염증 매개 물질의 생성을 야기하고 손상된 간에서 콜라겐 생성의 주요 역할을 하는 간성상세포를 직접적으로 활성화시키기도 한다42.
대부분의 경우 ALD는 증상이 거의 없어, 진단 시 임상적 의심, 검사실 검사 등에 의존한다. 간경변 환자의 신체검사에서 여성형 유방, 거미상 관절, 수장성홍반 등의 피부 증상이나 황달, 간성뇌증, 복수 등도 말기 간 질환 환자에게서 보일 수 있다. ALD의 진단은 하루에 40-50 g 이상의 과도한 알코올 섭취와 간 손상을 암시하는 위장관 출혈, 복수, 황달 등의 임상적 징후를 참고하게 된다3.
ALD에서 대부분의 환자들은 무증상의 알코올성 지방간을 이환 중이며 20-35%에서 간염이나 간경변으로 진행된다. ALD의 치료의 기본은 금주이며 초기에는 단순 금주로도 초기 알코올성 지방간을 해결할 수 있고 진행된 ALD의 환자에서도 생존율을 향상시킨다. ALD를 가진 환자의 대부분이 영양실조를 겪고 있어 단백질, 칼로리 등 영양 공급이 치료의 주요 단계 중 하나이다. 주로 코르티코스테로이드가 ALD에 전반적으로 사용되는 약물로 대부분에서 치료 효과를 나타내나 그에 반응하지 않는 40%의 환자에서 뚜렷한 치료대안이 없어 pentoxifylline, Anti-TNF therapy, 항산화제 등 새로운 치료법 개발을 위해 연구들이 진행되고 있다43.
한의학에서는 음주의 과도로 인한 내상을 酒傷이라 하였으며, 이에 관련되는 질환은 傷酒, 酒病, 酒疸, 酒積, 酒癖, 酒瘕, 酒鼓 등이 있다. 이 중 傷酒는 알코올성 지방간, 간염을, 酒癖은 중증 알코올성 간염, 알코올성 간경변, 酒鼓는 알코올성 간경화와 腹水로 볼 수 있다. 지속적인 음주는 肝, 腎, 脾에 영향을 미치는데 ALD 환자들이 호소하는 영양부족, 혈중 단백질 합성부족, 부종, 복수, 출혈 등의 증상들이 이 세 장기의 불균형 및 기능 부전에 의한다고 볼 수 있다. 이 세 장부가 虛損되면 血瘀癥積濕熱內蘊하여 긴 기간이 지나면 肝腎陰虛, 肝脾陰虛를 일으킨다. 치료로 發散, 利小便, 上下分消基濕을 기본으로 袪痰, 行氣, 消導 등의 치법을 사용할 수 있다. 관련 처방은 對金飮子, 葛花解酲湯, 酒積丸 등이 응용되고 있다5,23,40.
본 연구는 이제까지의 ALD에 대한 한의계의 연구 동향을 파악하고자 국내 데이터베이스를 통해 실험논문 8편, 임상연구 논문 26편, 고찰논문 3편 총 37편의 논문을 검색하여 이를 분석하였다.
연구의 유형은 사람을 대상으로 한 임상연구 논문이 전체 연구 수의 70.3%로 가장 많았고, 쥐를 대상으로 한 in vivo 실험 논문이 21.6%, 고찰논문이 8.1%를 차지하였다. 임상연구 논문 중에서 증례보고가 96%로 가장 많이 출판되었다. 국내에서 ALD에 대하여 1993년 최초로 논문이 발행 된 후 매년 평균 1.5편의 논문이 출판되었다. 2018년에 발표된 논문은 6편으로 가장 많았다. 또한 한의학 학회지가 아닌 곳에서 발행된 논문이 총 5편이었으며 모두 in vivo 실험 논문으로 한의학계 밖에서도 한약재, 한약을 통한 알코올성 간질환 치료에 주목하고 있음을 짐작할 수 있다.
임상 논문의 대상자를 살펴보면 대부분이 남성(94.3%)으로 평균나이는 53.5세, 50-60대가 44.4%를 차지하였다. 가장 자주 호소하는 임상 증상은 피로와 식욕부진, 소화불량이었으며 그 외에도 불면, 오심, 복수, 복부불편감, 현훈, 복통, 소양감, 황달, 협통 등을 호소하였으며 이는 기존에 알려진 ALD의 주증상과 일치하는 결과이다3.
ALD의 증례 보고 논문 중 변증을 명시한 논문은 14편으로 6편에서 肝膽濕熱로, 3편에서 濕熱, 脾胃濕熱, 濕熱內鬱로 변증하여 대부분의 연구에서(64.3%) ALD를 濕熱로 보고 치료했음을 확인할 수 있었다.
연구에서 쓰인 치료중재를 살펴보면 대부분 연구에서 탕약(88.5%)을 사용하였으며 그 다음이 침치료(57.7%)였다. 뜸과 부항치료는 부가적으로만 사용되었다.
탕약치료는 임상연구 논문 26편 중 23편에서 쓰였으며 특히 탕약 단독 치료를 치료중재로 사용한 연구가 9편이었다. 유일한 RCT 연구도 탕약의 효과를 밝히기 위한 시험이었다. 사용된 한약 처방은 총 23가지로 그 중 生肝健脾湯이 4편(17.4%), 淸肝解酒湯이 3편(13.0%)에서 사용되었다. 生肝健脾湯은 茵蔯五笭散과 加減胃笭湯을 합한 처방으로 利膽, 利尿, 健脾, 安胃하여 肝機能을 원활케 하는 목적으로 만든 처방이다. 임상에서 만성간염을 비롯한 제반 肝臟 疾患에 광범위하게 사용되고 있으며 간 기능 회복에 효과가 있음이 보고된 처방이다44-47. 淸肝解酒湯은 對金飮子와 茵蔯四苓散에 解酒毒의 要藥인 葛根, 赤楊 등을 더한 처방으로 임상에서 알코올성 간질환의 치료에 다용되며 이미 연구를 통해 알코올성 간손상으로 인한 각종 LFT 수치와 임상증상의 호전, 알코올 유도성 apoptosis 억제, 간세포 활성 호전, 알코올성 간손상으로 인한 섬유화 및 단백질 산화 억제, 산화스트레스에 대한 항산화 작용 등이 보고되어 있는 처방이다48-53. 가장 자주 쓰인 두 처방이 모두 알코올로 인한 濕熱을 치료한다는 점에서 대부분의 연구에서 ALD를 濕熱로 변증한 것과 일치함을 확인할 수 있었으나 23가지 처방 중 4회, 3회 언급된 生肝健脾湯과 淸肝解酒湯을 임상에서 알코올성 간질환의 치료에 대표되는 처방으로 보기에는 어려움이 있다. 한약을 치료 중재로 사용한 23편의 논문 중 사용된 처방이 23편이라는 것은 ALD의 치료에 있어 특효가 있는 처방이 밝혀지지 않은 것으로 판단되며 그와 관련된 연구가 더 필요할 것으로 보인다. 23가지 처방 중에서 가장 자주 사용된 약재는 19회 사용된 茯苓이었으며, 澤瀉가 14회로 두 번째였고 甘草, 白朮, 茵蔯이 13회, 生薑, 厚朴이 12회씩 사용되었다.
침 치료는 27편 중 15편(57.7%)에서 사용된 치료 방법으로 침과 약침을 병용한 논문이 3편, 전침과 약침을 병용한 논문 1편, 이침을 사용한 논문이 1편이었다. 침 치료시 언급된 혈위 50가지 중 中脘(CV12), 合谷(LI4), 太衝(LR3)과 足三里(ST36)가 6회로 12%씩 차지하였다. 대상 논문에서 다용된 혈위 모두 胃腸機能을 조절하고 祛濕利水하는 효과가 있어 소화기계의 치료에 자주 쓰이는 혈위라는 것이 특징적이다59. 그러나 논문간의 동질성이 확보되지 않았고 가장 많이 언급된 혈위가 12%에 불과하며 특히 단독 침 치료 연구 논문이 단 2편이었던 것을 고려해보면 알코올성 간질환의 침 치료 효과를 검증할 수 있는 추가적인 연구가 필요할 것으로 사료된다.
ALD의 치료 효과는 임상 증상의 호전도와 LFT로 평가할 수 있었는데 대부분의 연구에서 치료 종료 후 임상 증상들이 미약하거나 소실되었다. LFT의 경우 검사를 시행한 24편 중 3편7,20,36을 제외한 연구에서 측정한 모든 LFT 수치가 치료 후 개선되었으며 6편5,6,12,14,25,33의 연구에서 모든 수치가 정상 범위로 호전되어 ALD에 치료 유효성과 안정성에 대한 가능성을 보였다.
고찰 논문은 총 3편으로 김 등23은 알코올성 간질환에 대한 변증이 기술된 학술지 논문과 단행본을 고찰하여 ALD를 脾虛痰濕 및肝氣鬱結, 氣滯血瘀, 濕熱蘊結, 正虛型 네 가지 변증으로 분류하고 그 순서대로 유형별 발생 빈도가 높음을 밝혔다. 뿐만 아니라 김 등은 고찰연구에서 이 네 가지 변증 분류를 이용하여 변증 설문지를 구성하여 평가 척도 연구를 진행하였고 ALD의 변증 도구로 활용할 설문지의 초안을 제시26한 것에 의의가 있다. 고찰 논문 중 문헌 고찰 연구는 총 2편으로 2편 모두 현대의학에서의 ALD의 병리기전과 진단 및 치료를 정리함과 동시에 고문헌에서의 ALD의 병리기전을 고찰하고 한의학적 병변 기전과 치법, 처방을 정리하여 ALD에 대한 한의학적 치료의 접근을 모색하고자 하였다. 김40은 ALD의 다양한 임상적 양상을 한의학적 병증과 증후로 연결하고 發散, 利小便, 上下分消導其濕을 기본으로 하는 치법을 정리하여 ALD의 한의학적 치료의 기초자료를 마련하였다. 한 등38은 알코올성 간경변의 한의학적 병리기전을 정리하고 그에 대한 치법 및 대표적 처방을 확인하여 ALD의 치료방법을 모색하기 위한 한의학적 연구의 근거자료로서 의미가 있다. 또한 홍5은 알코올성 간질환의 임상증상을 호전시킨 증례를 보고한 논문에서 ALD의 한의학적 정의와 분류, 치료를 간단하게 고찰하여 보고한 점이 특징적이다.
본 논문에서 선정한 임상연구 논문을 살펴보면 대부분의 연구에서 ALD에 대한 한의학적 치료 후 복부불편감, 황달, 불면 등의 임상적 증후들의 호전 및 혈액검사 상에서 LFT 수치의 개선 등의 긍정적인 효과를 보고하였다. 특히 배 등7의 증례보고에서 금주를 실패한 경우를 제외하고 치료의 실패를 보고하거나 치료로 인한 부작용이 보고된 바가 없었다. 이것이 실제로 한방치료의 안정성이 높아 부작용이 발생하지 않은 것인지, 연구자의 보고 누락인지를 확인할 수 없기 때문에 이에 대한 추가적인 임상시험으로 치료의 유효성과 안정성 여부를 밝혀야 할 필요성이 있다. 또한 임상연구의 대부분이 증례보고에 그쳐 코호트 연구, 단면연구, 무작위임상시험 연구 등 앞으로 다양한 연구가 필요하며 치료 중재도 단순 한약 외에 침, 약침, 뜸 등 다양한 중재를 통하여 ALD에 대한 한의학적 치료 효과를 밝힐 필요성이 있다. 향후 연구에서는 본 연구를 바탕으로 실험실적 연구 및 개별 증례에서 효과를 보인 치료법을 근거로 하여 체계적인 대규모 임상시험의 시행이 필요할 것으로 사료된다. 본 연구는 ALD의 한의학적 치료에 대한 국내의 논문을 모두 포함하여 분석하여 ALD에 대한 국내 한의학계의 연구 경향을 파악하였으며 앞으로 보완 연구가 필요한 영역을 확인한 것에 의의가 있다. 그러나 논문의 질에 제한을 두지 않았고, ALD에 대한 무작위임상시험 연구가 부족하여 체계적 문헌고찰을 할 수 없었으며 ALD의 한의학적 치료의 객관적인 근거라고 말하기 어렵다는 한계가 있다. 이를 위해 추후 무작위임상시험과 체계적 문헌고찰 및 메타 분석 연구가 진행되어야 할 것으로 보인다.
V. 결 론
ALD의 한의학적 치료에 대한 국내 연구 동향을 살피기 위하여 관련 논문 37편을 분석한 결과 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
1. 총 37편의 논문 중 실험논문이 8편(21.6%), 임상연구 논문이 26편(70.3%), 고찰논문이 3편(8.1%)이었다. 그 중에서도 임상 연구 논문은 case report 17편(65.4%), case series 7편(26.9%), assessment scale(평가척도연구) 1편(3.8%), 무작위대조시험 1편(3.8%)이었다.
2. 실험 논문은 총 8편으로 모두 동물 실험이었으며 단일 본초 혹은 복합 한약처방에 대한 동물 단계에서의 효능 및 그 기전에 대한 연구가 이루어졌다.
3. 임상연구 논문에서 대상자 총 183명의평균나이는 53.5세로 50-60대가 44.4%를 차지하였고 남성의 비율이 94.3%로 여성보다 높았다.
4. 임상연구 논문 26편 중 가장 다용된 치료 중재는 한약이 88.5%, 침이 57.7%였다. 대부분 濕熱(64.3%)로 변증하였으며 처방은 生肝健脾湯(4편), 淸肝解酒湯(3편)이 가장 자주 사용되었고, 혈자리는 中脘(CV12), 合谷(LI4), 太衝(LR3), 足三里(ST36)이 가장 자주 사용되었다.
5. ALD의 임상증상과 LFT 수치개선에 한약, 침 등의 한의학적 치료의 유효성과 안정성에 대한 가능성을 제시하였다.
6. ALD에 대한 고찰논문은 ALD의 정의, 병인, 병리기전, 치방 등에 대한 문헌적 고찰연구 뿐만 아니라 ALD의 한의학적 평가 척도 연구도 이루어졌다.