중풍환자의 통증 치료에 관한 체계적 고찰 연구
Abstract
Objectives
Strokes have diverse symptoms and signs. One of ten stroke patients has chronic pain after a stroke. Pain after a stroke interrupts rehabilitation and worsens quality of life, but there is no efficient treatment for this pain. This study surveyed and reports on the clinical studies of treatment for chronic pain after a stroke.
Methods
We searched journals for reports on clinical studies of treatment for chronic pain after a stroke through the databases OASIS ( http://oasis.kiom.re.kr), NDSL (ndsl.kr), Kmbase ( http://kmbase.medric.or.kr/), and PubMed ( http://www.pubmed.com). The search words were “stroke & pain”, “jungpung中風 & pain”, “pungbi風痺”, “cerebral hemorrhage & pain”, and “cerebral infarction & pain”.
Results
Twenty-nine studies of treatment for chronic pain after a stroke were found. Of these, 15 were randomized controlled trials, 10 were nonrandomized controlled trials, and 4 were “before and after” studies. Treatments were diverse, including acupuncture, electroacupuncture, herbal acupuncture, herbal medicine, and more. The treatment periods were longer than 3 weeks on average.
Conclusions
These results show that good quality randomized controlled trials of treatment for chronic pain after a stroke are small in number. We need larger and more diverse studies of treatment for chronic pain after a stroke.
Keywords: stroke, chronic, pain, treatment
I. 서 론
중풍(뇌졸중)은 뇌혈관에서 출혈이나 경색으로 인하여 뇌로 가는 혈류 공급이 원활하지 않아, 뇌조직이 괴사되어 신경학적 결손증상이 24시간 이상 지속되는 경우를 말한다. 우리나라를 포함하여 전세계적으로 중풍은 사망원인과 장애요인 수위를 차지하고 있다. 중풍으로 인한 인구 사회학적 비용은 매우 많다고 알려져 있다. 최근 우리나라는 고령화 사회 및 초고령화 사회 진입으로 인하여, 중풍의 유병률 및 사망률은 증가할 것으로 예측되고 있기 때문에 이에 대한 예방과 대비책이 필요하다.
중풍은 반신마비, 연하장애, 구음장애, 감각이상, 두통, 어지럼증, 시야장애 등 다양한 증상을 가진다. 그 중 가장 흔한 증상은 반신마비로 장애를 가지게 되지만, 중풍환자의 만성 통증은 약 10명중 1명에게서 있는 것으로 나타나는데, 견관절 아탈구, central post stroke pain, 시상 증후군, 근골격계 통증 등 다양한 원인으로 발생한다 1-4. 이러한 중풍후 통증은 환자에게서 삶의 질을 낮추고, 재활에 방해가 된다. 그렇지만, 중풍 통증에 대해 유효한 양의학적 치료법은 없는 상황이며, 환자들은 고통 받고 있는 실정이다. 따라서, 중풍 환자의 통증을 관리하기 위해서 기존의 논문을 검색해보고, 유용한 치료방법을 정리하고, 안전성 유효성을 살펴보기 위하여 본 연구를 실시하였다.
II. 연구대상 및 방법
1. Database 선정 및 기간
1) 검색엔진
OASIS(전통의학정보포털), NDSL(국가과학기술정보센터), Kmbase(한국의학논문 데이터베이스), Pubmed를 검색엔진으로 활용하였으며, 2015년 8월 1일까지 검색하였다.
2) 검색식 및 결과
OASIS에서는 중풍+통증, 뇌졸중+통증, 풍비, 뇌출혈+통증, 뇌경색+통증을 검색식으로 하였다. 결과는 각 검색식별로 각 6편, 8편, 8편, 1편, 0편으로 총 24편이었다.
NDSL에서는 (중풍 and 통증) or (뇌졸중 and 통증) or (뇌경색 and 통증) or (뇌출혈 and 통증) or 풍비를 검색식으로 하였다. 결과는 총 35편이었다.
한국의학논문데이터베이스(Kmbase)에서는 (중풍 or 뇌졸중 or 뇌경색 or 뇌출혈) and 통증으로 검색시에 총 56편이었다.
Pubmed에서는 많은 논문이 검색되어, limit으로 clinical trial, title, free full text, 5년 이내 논문으로 제한하였다. 검색식으로는 (stroke or cerebral infarction or hemorrhage) and pain으로 검색하여 총 17편의 논문이 검색되었다. 모든 논문을 합한 결과 132편이었으며, 중복논문을 29편을 제외하고 103편이 나왔다.
3) 논문 선정 및 제외기준
(1) 선정기준
① 국제질병분류상 I61부터 I69에 해당하는 질환
② 통증이 주제인 논문
③ 임상시험이나 임상관련 논문
(2) 제외기준
① I61~I69에 해당하지 않는 논문
② 논문의 주제가 통증이 아닌 논문
③ 실험관련 논문
④ 논문 원본을 구할 수 없는 논문
중풍 환자 통증관련 논문에 대해 연구자들이 이중 체크하여 선정하였으며, 논란이 되는 경우 합의하여 선정 제외하였다. 이중 중풍 관련 아닌 것, 문헌고찰, 임상시험이 아닌 것 74편을 제외하고, 총 29편의 논문을 선정하였다. 그 중에서 무작위 임상시험은 15편이 있었다( Fig. 1).
Fig. 1
Searching process of articles. 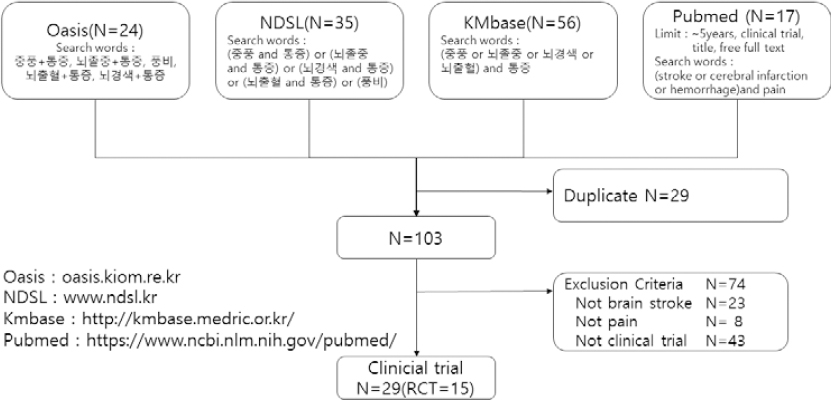
III. 결 과
1. 중풍 통증 임상시험 연구디자인 종류 및 출판연도
중풍 통증 임상시험 논문은 총 29편으로 무작위대조군 연구 15편, 비무작위대조군 연구 논문 10편, 전후비교연구와 증례보고 논문이 4편이었다. 국내 중풍 통증 관련 논문은 1998년부터 논문은 발간되었으며, 무작위 임상시험은 2003년부터 실시되었다( Table 1).
Table 1
Study Design & Published Year in Inclusion Articles
|
1998 |
2001 |
2002 |
2003 |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
Total |
|
RCT |
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
2 |
2 |
|
2 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
15 |
|
NCT |
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
10 |
|
B&A |
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
Total |
1 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
5 |
4 |
1 |
29 |
Table 2
Study Design and Pain Type in Included Articles
|
RCT |
NCT |
B&A |
Total |
|
Upper limb pain |
11 |
4 |
1 |
16 |
|
CPSP |
2 |
5 |
3 |
10 |
|
CRPS I |
2 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
|
General pain |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
|
Total |
15 |
10 |
4 |
29 |
Table 3
Study Design & Published Year in Inclusion Articles
|
Acupuncture |
Massage |
Stretching |
Botolinum |
Nerve block |
Taping |
Etc. |
|
RCT |
5 |
|
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
4 |
|
NCT |
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
1 |
5 |
|
B&A |
1 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
Total |
6 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
10 |
2. 연구대상자 수
보고된 중풍 통증 임상시험 논문은 시험대상자가 평균 43.5명으로 적게는 12명에서 많게는 189명을 대상으로 이루어졌다. 그러나 국내 무작위 대조시험 중 100명을 넘기는 대단위 시험은 없었다( Table 4).
Table 4
Characters of Upper Limb Pain after Stroke in Included Articles
|
Title |
Articles |
Journal |
Publish |
Sample Size |
Study design |
Intervention |
Period |
Frequency |
Effect |
|
Suprascapular nerve block for shoulder pain in the first year after stroke: a randomized controlled trial |
Adey- Wakeling Z et al5
|
Stroke |
2013 |
57 |
RCT |
Nerve block |
1 time |
1 time |
Yes |
|
|
Effects of scapular taping on muscle activity, pain, range of motion and proprioception in subacute stroke patients |
Lee JN et al6
|
Kor. Aca-indusl co Soc |
2013 |
28 |
RCT |
Taping |
1 time |
1 time |
Yes |
|
|
Randomized controlled study of segmental neuromyotherapy for post-stroke hemiplegic shoulder pain |
Motti et al7
|
J Rehabil Med |
2012 |
24 |
RCT |
Occupunctional therapy and physiotherapy |
4 weeks |
5 days/wk |
Yes |
|
|
The comparative Study of effectiveness of cotreatment with samgieum-gagam, acupucture and sweet bee venom acupuncture on post-stroke shoulder pain |
Cho SH et al8
|
Kor Acu & Moxi Soc |
2012 |
43 |
RCT |
Herbal acupuncture |
4 weeks |
3 days/wk |
Yes |
|
|
Botulinum Toxin for the Upper Limb after Stroke(BoTULS) Trial :effect on impairment, activity limitation, and pain |
Shaw LC et al9
|
Stroke |
2011 |
189 |
RCT |
Botulinum |
1 time |
1 time |
Yes |
|
|
Does suprascapular nerve block reduce shoulder pain following stroke: a double-blind randomised controlled trial with masked outcome assessment |
Allen ZA et al10
|
BMC Neurology |
2010 |
66 |
RCT |
Subscapular nerve block |
1 time |
1 time |
Yes |
|
|
The effectiveness of Zingiberis Rhizoma herbal acupuncture therapy and bee venom herbal acupuncture therapy for treating post-stroke hemiplegic shoulder pain |
Cho SW et al11
|
J Orient Rehabil Med |
2005 |
23 |
RCT |
Herbal acupuncture |
2 weeks |
3 times/wk |
Yes |
|
|
Is botulinum toxin type A effective in the treatment of spastic shoulder pain in patients after stroke? A double-blind randomized clinical trial |
Marco E et al12
|
J Rehabil Med |
2007 |
29 |
RCT |
Botulinum |
1 time |
1 time |
Yes |
|
|
Effectiveness of bee venom acupuncture on shoulder pain after stroke |
Ko CN et al13
|
J Kor Orient Med |
2007 |
43 |
RCT |
Herbal acupuncture |
2 weeks |
3 times/wk |
Yes |
|
|
Pain, fatigue, and intensity of practice in people with stroke who are receiving constraint-induced movement therapy |
Underwood J et al14
|
Physical therapy |
2006 |
32 |
RCT |
Movement therapy |
10 days |
1 times/day |
Yes |
|
|
Combined arm stretch positioning and neuromuscular electrical stimulation during rehabilitation does not improve range of motion, shoulder pain or function in patients after stroke: a randomised trial |
deJong LD et al15
|
J Physiother |
2013 |
46 |
RCT |
Stretching +NMES |
8 weeks |
2 sessions /day, 5 days/wk |
No |
|
|
The effetcs of rehabilitation training using video game on improvement range of motion for upper-extremity, shoulder pain and stress in stroke patients with hemiplegia. |
Byun PS16
|
J muscle joint health |
2012 |
56 |
NCT |
Game |
3 weeks |
5 times/wk |
Yes |
|
|
A Pilot study on the effect of aroma massage on stroke patients upper aArm pain |
Park JE et al17
|
Kor Clinic. Nur. Research |
2004 |
15 |
NCT |
Massage |
6 days |
1 times/day |
Yes |
|
|
Effects of a taping therapy on shoulder range of motion and pain, physical function and depression of stroke patients with hemiplegia |
Kang SJ et al18
|
Kor Clinic. Nur. Research |
2012 |
50 |
NCT |
Taping |
8 weeks |
2 times/wk |
Yes |
|
|
The influences of Chuna(shoulder traction) therapy for shoulder pain and range of movement in hemiplegic patients after stroke |
Kim MB et al19
|
J Oriental Rehab Med |
2007 |
50 |
NCT |
Chuna therapy |
2 weeks |
1 time/day (10 times/wk) |
Yes |
|
|
The effect of massage as a nursing intervention on central pain & skin temperature of stroke patients |
Han KS et al20
|
Kor Clinic. Nur. Research |
2001 |
12 |
B&A |
Massage |
5 weeks |
2 times/wk |
Yes |
3. 통증 종류
중풍 통증 임상시험 논문 중 통증에 따른 분류시 상지 통증이 16편으로 제일 많았다. 그 외 중풍후 중추성 통증 10편, 만성 복합부위 통증 증후군 2편, 일반 통증에 관한 논문 1편이 있었다( Table 2).
4. 처치의 종류
전체적으로 침치료 6편, 마사지 4편, 스트레칭 3편, 보툴리즘 2편, 신경차단 2편, 테이핑이 각각 2편의 논문이었다. 또한 무작위대조군연구에서도 침치료 연구논문이 가장 많은 5편이었다( Table 3).
5. 중풍후 발생한 상지부 통증에 관한 논문
중풍 후 발생한 상지부 통증에 관한 논문은 총 16편이었다. 무작위 대조군 연구는 11편이었으며, 한 개의 연구가 효과가 없는 것으로 나왔다( Table 4).
6. 중풍 후 발생한 central post stroke pain에 관한 논문
중풍 후 발생한 central post stroke pain에 관한 논문은 총 10편이었다. 무작위 대조군 연구는 2편, 비무작위연구는 5편, 전후비교연구는 3편이었으며 모두 효과가 있는 것으로 나타났다( Table 5).
Table 5
Characters of Central Post Stroke Pain in Included Articles
|
Title |
Articles |
Journal |
Publish |
Sample Size |
Study design |
Intervention |
Period |
Frequency |
Effect |
|
Efficacy of bee-venom acupuncture on central post stroke pain |
Kwak JY et al21
|
Kor Acu & Moxi Soc |
2009 |
19 |
RCT |
Acupuncture |
3 weeks |
2 times/wk |
Yes |
|
|
Specific electric acupuncture for the management of the central post stroke pain |
Choi DW et al22
|
Regional anesthesia and pain med |
2003 |
70 |
RCT |
Electric acupuncture |
4 weeks |
2 times/wk |
Yes |
|
|
Analgesic effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on central post-stroke pain |
Bae SH et al23
|
Tohoku J. Exp. Med |
2014 |
14 |
NCT |
Stretching |
3 weeks |
3 day/wk |
Yes |
|
|
Effect of JU Movement Therapy in Pain and Depression for Post-Stroke Hemiplegia |
Jeon HJ et al24
|
Kor J Sports Sci. |
2013 |
24 |
NCT |
Movement therapy |
12 weeks |
3 times/day |
Yes |
|
|
The effects of foot reflexology massage on the central pain fatigue, sleep in stroke patients |
Sung MH et al23
|
Kor Clinic. Nur. Research |
2011 |
48 |
NCT |
Massage |
1 month |
1 times/day |
Yes |
|
|
The clinical evaluation of east-west medical management for central poststroke pain |
Cheong BS et al26
|
J Pharmacopuncture |
2001 |
30 |
NCT |
East-west medical manage |
3 weeks |
- |
Yes |
|
|
A study on the effects of relaxation technique on attendant stress, pain and depression of hemiplegic patients |
Han JS et al27
|
Chung-Ang J Nursing |
1998 |
58 |
NCT |
Stretching |
3 weeks |
1 times/day |
Yes |
|
|
The effects of aroma massage therapy on post stroke central pain and depression |
Kim JE et al28
|
J Kyungpook Nursing Science |
2008 |
20 |
B&A |
Massage |
5 weeks |
2 times/wk |
Yes |
|
|
Clinical Study on the Effect of bee venom acupuncture therapy on the poststroke pain |
Jung KS et al29
|
Kor Acu & Moxi Soc |
2005 |
20 |
B&A |
Herbal acupuncture |
3 weeks |
1 times /2 day |
Yes |
|
|
Effectiveness of pain management for central poststroke pain on rehabilitation |
Lee DI et al30
|
The Korean J. Pain |
2002 |
30 |
B&A |
Pain treatment |
3 weeks |
- |
Yes |
7. 중풍 후 발생한 complex regional pain syndrome에 관한 논문
중풍 후 발생한 complex regional pain syndrome에 관한 논문은 총 2편으로 모두 무작위대조군연구이며, 모두 효과가 있는 것으로 나타났다( Table 6).
Table 6
Characters of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome in Included Articles
|
Title |
Articles |
Journal |
Publish |
Sample Size |
Study design |
Intervention |
Period |
Frequency |
Effect |
|
Mirror therapy for chronic complex regional pain syndrome type 1 and stroke |
Cacchio A et al31
|
N Engl J Med |
2009 |
24 |
RCT |
Mirror therapy |
8 weeks |
1 times/day |
Yes |
|
|
Comparison of prednisolone with piroxicam in complex regional pain syndrome following stroke: a randomized controlled trial |
Kalita J et al32
|
QJM |
2006 |
60 |
RCT |
Prednisolone /piroxicam |
1 month |
1 times/day |
Yes |
IV. 고 찰
중풍(뇌졸중)은 뇌혈관의 이상으로 뇌조직이 괴사되어 신경학적 결손 증상이 24시간 이상 지속되는 경우로, 사망과 장애의 주요요인이며, 많은 인구사회학적 비용을 발생시킨다.
중풍은 반신마비, 감각이상, 두통, 어지럼증, 복시, 구토 등 다양한 증상을 가진다. 그 중 중풍환자의 만성 통증은 견관절 아탈구, central post stroke pain, 시상 증후군, 근골격계 통증 등 여러 원인으로 발생한다. 이러한 중풍후 통증은 중풍 환자의 재활치료를 방해하고, 우울감을 유발하며, 환자와 보호자의 삶의 질을 낮추고 일상생활에 불편감을 주는 주요요인이다. 중풍환자의 통증 유병률에 대한 연구에서 흥미로운 사실은 통증이 시기별로 다르다는 것이다. Lund stroke resister에 따르면 중풍환자의 통증은 시간이 지날수록 유병률이 감소하지만, 통증강도가 심해지는 특징이 있다. 또한 중풍환자에서 통증은 나이가 어리거나, 여성, 중등도, 당화혈색소가 증가할수록 통증이 증가하는 경향을 보였다. 또한 16개월 뒤 추적조사결과에 따르면 우울증 환자나 여성 환자가 통증이 증가하는 것을 관찰 할 수 있다 33. 또한 중풍 환자는 중풍 발병 이전에도 약 50%에서 통증을 가지고 있지만, 중풍 발병 이후 어깨통증, 관절통증 등도 증가한다는 결과를 보이고 있다 34. Sommerfeld DK et al. 등의 연구를 살펴보면 중풍 발생시 통증이 없었지만, 3개월 후에 새롭게 통증이 있는 환자가 20명/91명이고, 18개월 후에는 11명/20명에서 통증이 발생하는 것으로 나타났다. 이렇듯 중풍이 발생시 통증이 없다고 소홀하면 안 되고, 지속적으로 중풍 환자의 통증 유무를 조사해야 한다 35. 중풍 발생이전 만성통증이 없는 15,754명을 추적 조사한 PRoFESS Trial에서는 중풍 환자중 통증이 있는 경우는 약 10.6%이며, 중풍후 중추성 통증이 약 2.7%, 말초신경 통증이 1.5%, 강직으로 인한 통증 1.3%, 어깨 아탈구 통증으로 인한 통증이 약 0.6%로 조사되었다. 중풍환자의 통증 중 중풍 후 중추성 통증의 예측인자로는 나이, 우울증, 중풍의 심함이 나타났고, 말초신경병증으로는 BMI, 흡연, 우울증, 소공성경색이, 강직과 아탈구 통증 예측인자로는 연령과 우울증, 중풍의 중등도 등이 나타났다 1. 이렇듯 중풍환자의 통증을 관찰하기 위해서는 주기적으로 장기적으로 관리해야 하며, 통증의 위험인자를 조사하며, 치료시 대비하는 것이 합리적이라 생각된다. 그렇지만, 중풍 환자를 치료하면서, 호소하는 만성 통증은 환자에 따라 한의학적 양의학적으로 치료하기 어려운 경우가 많으며, 효율적인 치료방법이 없는 것이 사실이다. 따라서 본 연구는 중풍 환자 통증 관리에 대한 기존 논문 검색과 유용한 치료방법을 정리하여, 중풍 환자 통증 관리에 대한 안전성과 유효성을 살펴보고자 하였다.
이를 위해서 OASIS(전통의학정보포털), NDSL (국가과학기술정보센터), Kmbase(한국의학논문 데이터베이스), Pubmed를 검색엔진으로 활용하였으며, 2015년 8월 1일까지 검색하였다.
OASIS에서는 중풍+통증, 뇌졸중+통증, 풍비, 뇌출혈+통증, 뇌경색+통증을 검색식으로 하였다. 결과는 각 검색식별로 각 6편, 8편, 8편, 1편, 0편으로 총 24편이었다. 비증에 대해서는 ≪素問⋅痹論≫ : “風寒濕三氣雜至, 合而為痹也. 其風氣勝者為行痹.”, ≪雜病證治準繩≫ : “風痹者, 遊行上下, 隨其虛邪與血氣相搏, 聚於關節, 筋脈弛縱而不收.”, ≪症因脈治≫卷三 : “風痹之症, 走注疼痛, 上下左右, 行而不定, 故名行痹.”이라고 하였다. 또한 唐代의 孫思邈은 ≪千金要方·論雜風狀≫에서 “中風 又名”卒中”, 以猝然昏仆, 口眼喎斜, 半身不遂爲 主要臨 床特點. ……一曰偏枯, ……四曰風痹, 表現爲肌膚麻木, 皮膚感覺異常, 骨節酸楚活動不利等. 目前臨床關於中風 皆沿用仲景之中經絡, 臟腑的分類.”이라고 하였다. 따라서, 본 논문에서는 손사막의 의견을 따라 風痺만을 검색하였다.
NDSL에서는 (중풍 and 통증) or (뇌졸중 and 통증) or (뇌경색 and 통증) or (뇌출혈 and 통증) or 풍비를 검색어로 활용하였다. 결과는 총 35편이었다.
한국의학논문데이터베이스(Kmbase)에서는 (중풍 or 뇌졸중 or 뇌경색 or 뇌출혈) and 통증으로 검색시에 총 56편이었다.
Pubmed에서는 많은 논문이 검색되어, limit으로 clinical trial, title, free full text, 5년 이내 논문으로 제한하였다. 의학의 발달을 생각했을 때 5년 이상 지난 논문은 현재 사용하는데 한계가 있다고 생각하였기 때문이다. 검색식으로는 (stroke or cerebral infarction or hemorrhage) and pain으로 검색하여 총 17편의 논문이 검색되었다. 모든 논문을 합한 결과 132편이었으며, 중복논문을 29편을 제외하고 103편이 나왔다.
중풍 환자 통증관련 논문에 대해 연구자들이 이중 체크하여 선정하였으며, 논란이 되는 경우 합의하여 선정 제외하였다. 이중 중풍 관련 아닌 것, 문헌고찰, 임상시험이 아닌 것 74편을 제외하고, 총 29편의 논문을 선정하였다. 그중 상지부 통증 논문이 16편, 중풍 후 중추성 통증 논문 10편, 복합부위통증 증후군 논문 2편, 그 외 중풍환자의 삶의 질과 일반적 통증에 대한 논문 1편이 있었다. PRoFESS Trial에서 어깨통증이 가장 적었지만, 실제 연구로는 어깨 통증이 가장 많이 활용된 것은 X-ray 등 진단기기와 아탈구의 정도를 측정할 수 있는 방법, 중풍 후 중추성 통증 등은 시각상사척도 등 주관적인 경우로 주로 측정되기 때문이라 생각된다. 중풍 환자의 어깨 통증에 대한 유병률은 단기 장기 합하여, 9%~84%로 매우 다양하게 나타나며, 평균 2.26개의 원인이 있다고 알려져 있다 36. 어깨 통증에 대한 치료 연구들을 신경차단술, 테이핑요법, 보튤리즘 주사 등은 1회 시술을 통한 연구와 길게는 8주 시술까지 하는 이완요법, 운동 요법 등이 나타났다. 총 16편의 논문 중 15편이 효과가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 효과가 없는 근육이완요법의 논문이 8주까지 치료하였으나 효과가 없는 1편이었다. 중풍 후 발생한 중추성 통증은 중풍환자들이 호소하는 주요 증상중의 하나이다. 일반적으로 중추성 통증은 시상 증후군에 의해 주로 나타나고, 운동장애가 심하지 않는 특징이 있어서 주변 사람들은 알아주지 않고, 환자 본인만 느끼는 자각증상이므로, 우울감에 빠지기 쉽다. 韓醫學에서는 風痺에 해당하는데, 정 등 38의 연구에서는 陰虛陽亢證, 血瘀證, 火熱證이 다수를 차지한다고 하였다. 이에 대한 연구는 총 10편의 논문이 선정되었는데, 무작위 연구는 2편으로 적었다. 10편의 연구결과 모두 효과가 있는 것으로 나타났지만, 치료기간은 최소 3주 이상이었으며, 침 치료의 경우는 최소 1주일에 2번 이상 지속시 효과가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 이러한 결과를 볼 때 중풍환자의 중추성 통증에 대해서는 환자에게 미리 충분히 시간이 소요됨을 알리고 치료를 시행하는 것이 좋다고 생각된다. 중풍 후 복합부위통증증후군에 대한 논문은 2편이 검색되었으며, 모두 무작위대조군연구이며, 모두 효과가 있는 것으로 나타났지만, 8주 이상의 치료기간이 소요된다고 하였다. 여기서 눈여겨 봐야할 것은 매일 하루에 한번씩 8주간 시행한 거울요법이다. 최근 이미지 치료법에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있는데, 거울요법, 이미지 요법 등에 대한 효용도가 높아지고 있는 상황이다.
또한 연구결과에 정리되지 않았지만, 중풍환자의 전반적 통증에 관하여 주당 5회, 2달간 실시한 ‘낮병원 관리 프로그램’을 실시한 박 등 39의 논문이 있었다. ‘낮병원’이란 낮 시간 동안 병원에 머무르는 부분 입원의 형태로, 오전 9시-오후 5시 동안 진행된다. 자세한 프로그램은 의료(의료 : 재활의학전문의진찰, 상담, 투약, 물리치료, 작업치료, 언어치료, 재활간호), 재활교육(주 1회 물리치료, 작업치료, 언어치료, 재활간호 교육을 통한 장애심화, 합병증 예방 및 자각관리능력 함양), 그룹 활동(재활 스포츠 활동, 원예치료), 심리, 사회적서비스(사회사업상담, 심리평가 및 상담, 소그룹 부부 상담, 가족상담), 영화관람 쇼핑 등 사회 적응 훈련으로 구성되어있다. 82명이 참가하였으며, 대조군에 비하여 치료군에서 통증을 포함한 여러 변수에서 유의한 효과가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 최근 1인 가족 등으로 인하여 중풍환자 돌보기가 힘들어지는 상황에서 집단적으로 ‘낮병원 관리 프로그램’을 활용하는 것은 개인이나 가정뿐만이 아니라, 사회적 비용을 줄일 것으로 기대되며, 향후 이 같은 프로그램이 지역공중보건으로 개발되어야 할 것이라 생각된다.
V. 결 론
중풍환자의 만성 통증 관리를 위하여 본 연구를 실시하였다.
검색 결과 중복을 제외하고 103편이 검색되었으며, 선정기준에 적합한 논문은 총 29편이었다. 무작위대조군연구가 가장 많으며, 비무작위연구, 전후비교연구순으로 나타났고, 어깨 관절에 관한 통증, 중풍후 중추성 통증, 복합부위증후군의 빈도로 연구되었다. 치료에 대한 논문은 신경차단술 같은 경우 1회 시술로 끝나는 경우가 있지만, 최소 주 2회 이상, 3주 이상의 방법을 사용한 것이 많았다. 중풍 환자의 통증에 관한 연구의 경우 역학조사는 대규모인 것에 비하여, 임상시험논문은 연구대상자 수가 적고, 일반화하기 어려운 특성이 있다고 판단된다.
향후 체계적인 RCT 논문들이 추가된다면 중풍 후 만성적 통증을 겪는 환자들에게 더욱 효과적인 치료를 할 수 있을 것이다.
감사의 말씀
본 연구는 세명대학교한의과대학 2014년도 교내연구비 지원을 받았기에 감사의 뜻을 전합니다.
참고문헌
1. O’Donnell MJ, Diener HC, Sacco RL, Panju AA, Vinisko R, Yusuf S. PRoFESS Investigators. Chronic pain syndromes after ischemic stroke: PRoFESS trial. Stroke 2013:44(5):1238–43.   2. Pandian JD, Kaur P, Arora R, Vishwambaran DK, Toor G, Mathangi S, et al. Shoulder taping reduces injury and pain in stroke patients: randomized controlled trial. Neurology 2013:80(6):528–32.   3. Sprenger T, Seifert CL, Valet M, Andreou AP, Foerschler A, Zimmer C, et al. Assessing the risk of central post-stroke pain of thalamic origin by lesion mapping. Brain 2012:135(Pt 8):2536–45.   4. Bae SH, Kim GD, Kim KY. Analgesic effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on central post-stroke pain. Tohoku J Exp Med 2014:234(3):189–95.   5. Adey-Wakeling Z, Crotty M, Shanahan EM. Suprascapular nerve block for shoulder pain in the first year after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2013:44(31):3136–41.   6. Lee JN, Lim JK. Effects of scapular taping on muscle activity, pain, range of motion and proprioception in subacute stroke patients. Journal of the Korea Academia-industrial cooperation Society 2013:14(11):5689–97.  7. Ratmansky M, Defrin R, Soroker N. Randomized controlled study of segmental neuromyotherapy for post-stroke hemiplegic shoulder pain. J Rehabil Med 2012:44(10):830–6.   8. Cho SH, Cho HS, Lee KY, Yun SH, Jung WS, Kim SH. The comparative Study of effectiveness of cotreatment with samgieum-gagam, acupucture and sweet bee venom acupuncture on post-stroke shoulder pain. The journal of Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Medicine Society 2012:29(2):15–27.
9. Shaw LC, Price CI, van Wijck FM, Shackley P, Steen N, Barnes MP, et al. BoTULS Investigators. Botulinum Toxin for the Upper Limb after Stroke (BoTULS) Trial: effect on impairment, activity limitation, and pain. Stroke 2011:42(5):1371–9.   11. Cho SW, Go KH, Nam JH, Kim MS, Lee SY, Lee IS, et al. The effectiveness of Zingiberis Rhizoma herbal acupuncture therapy and bee venom herbal acupuncture therapy for treating post-stroke hemiplegic shoulder pain. J Orient Rehabil Med 2005:15(4):77–87.
12. Marco E, Duarte E, Vila J, Tejero M, Guillen A, Boza R, et al. Is botulinum toxin type A effective in the treatment of spastic shoulder pain in patients after stroke? A double-blind randomized clinical trial. J Rehabil Med 2007:39(6):440–7.   13. Ko CN, Min IK, Park SW, Jung WS, Moon SK, Park JM, et al. Effectiveness of bee venom acupuncture on shoulder pain after stroke. J Kor Orient Med 2007:28(1):11–24.
14. Underwood J, Clark PC, Blanton S, Aycock DM, Wolf SL. Pain, fatigue, and intensity of practice in people with stroke who are receiving constraint-induced movement therapy. Physical therapy 2006:86:1241–50.   15. de Jong LD, Dijkstra PU, Gerritsen J, Geurts AC, Postema K. Combined arm stretch positioning and neuromuscular electrical stimulation during rehabilitation does not improve range of motion, shoulder pain or function in patients after stroke: a randomised trial. J Physiother 2013:59(4):245–54.   16. Buyn PS, Chon MY. The effetcs of rehabilitation training using video game on improvement range of motion for upper-extremity, shoulder pain and stress in stroke patients with hemiplegia. J muscle joint health 2012:19(1):46–56.  17. Park JE, Kim MA. A Pilot study on the effect of aroma massage on stroke patients upper aArm pain. Korean Clinical Nursing Research 2004:10(1):184–95.
18. Kang SJ, Kim IS. Effects of a taping therapy on shoulder range of motion and pain, physical function and depression of stroke patients with hemiplegia. Korean J Adult Nursing 2012:5(1):294–304.  19. Kim MB, Chung SH, Kim SS. The influences of Chuna(shoulder traction) therapy for shoulder pain and range of movement in hemiplegic patients after stroke. J Oriental Rehab Med 2007:17(2):185–98.
20. Han KS, Kim SM, Park JS. The effect of massage as a nursing intervention on central pain & skin temperature of stroke patients. Korean Clinical Nursing Research 2001:7(2):55–66.
21. Gwak JY, Cho SY, Shin AS, Lee IH, Kim NH, Kim HM, et al. Efficacy of bee-venom acupuncture on central post stroke pain. The J Korean Acupuncture and Moxibustion Society 2009:26(6):205–14.
22. Choi DY. Specific electric acupuncture for the management of the central post stroke pain. Regional anesthesia and pain med 2003:28(suppl):65.  23. Bae SH, Kim GD, Kim KY. Analgesic effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on central post-stroke pain. Tohoku J. Exp. Med 2014:234(3):189–95.   24. Jeon HJ, Back JH. Effects of JU movement therapy in pain and depression for post-stroke hemiplegia. Kor J Sports Science 2013:22(3):1013–23.
25. Sung MH, Lee MH, Song GS, Jeon EM. The effects of foot reflexology massage on the central pain fatigue, sleep in stroke patients. J Korean Clinical nursing research 2011:17(1):46–56.
26. Cheong BS, Kim KS, Lee DI, Choi DY. The clinical evaluation of east-west medical management for central poststroke pain. J Pharmacopuncture 2001:4(2):95–103.  27. Han JS, Park KS. A study on the effects of relaxation technique on attendant stress, pain and depression of hemiplegic patients. Chung-Ang J Nursing 1998:2(1):97–109.
28. Kim JE, Seo SR. The effects of aroma massage therapy on post stroke central pain and depression. J Kyungpook Nursing Science 2008:12(1):23–34.
29. Jeoung KS, Kim SH, Park SK, Lim HJ, Yoon HS, Ahn HJ. Clinical Study on the Effect of bee venom acupuncture therapy on the poststroke pain. The J Korean Acupuncture & Moxibustion Society 2005:22(3):69–75.
30. Lee DI, Kim KS, Chae HS, Choi DY, Lee JD, Lee YH, et al. Effectiveness of pain management for central poststroke pain on rehabilitation. The Korean J Pain 2002:15(1):63–8.
31. Cacchio A, De Blasis E, Necozione S, di Orio F, Santilli V. Mirror therapy for chronic complex regional pain syndrome type 1 and stroke. N Engl J Med 2009:361(6):634–6.   32. Kalita J, Vajpayee A, Misra UK. Comparison of prednisolone with piroxicam in complex regional pain syndrome following stroke: a randomized controlled trial. QJM 2006:99(2):89–95.   33. Jönsson AC, Lindgren I, Hallström B, Norrving B, Lindgren A. Prevalence and intensity of pain after stroke: a population based study focusing on patients’ perspectives. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2006:77(5):590–5.   34. Hansen AP, Marcussen NS, Klit H, Andersen G, Finnerup NB, Jensen TS. Pain following stroke: a prospective study. Eur J Pain 2012:16(8):1128–36.   35. Sommerfeld DK, Welmer AK. Pain following stroke, initially and at 3 and 18 months after stroke, and its association with other disabilities. Eur J Neurol 2012:19(10):1325–30.   36. Yoon TS, Kim DH, Park JW, Kwon BS, Ryu KH, Lee HJ, et al. Causes of the hemiplegic shoulder pain. J Korean Aca rehabil med 2010:34(2):158–62.
37. Viana R, Pereira S, Mehta S, Miller T, Teasell R. Evidence for therapeutic interventions for hemiplegic shoulder pain during the chronic stage of stroke: a review. Top Stroke Rehabil 2012:19(6):514–22.   38. Jeong EJ, Roh JH, Moon SK, Cho KH, Kim YS, Bae HS, et al. Clinical study of paraesthesia in stroke patients. J Korean Oriental Med 2001:22(2):41–52.
39. Park CS, Song BH. Effect of K-ADL·K-IADL and Quality of life in Day Hospital Program for Stroke Patients. J of the Korea Contents Association 2012:12(11):267–77. 
|
|